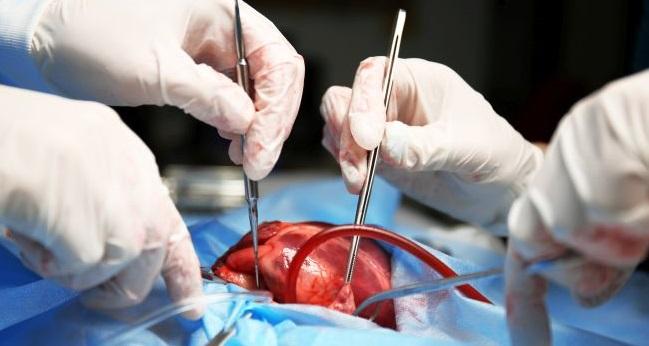
A coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary heart disease. It diverts blood around narrowed or clogged parts of the major arteries to improve blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart. It's used for people who have severe coronary heart disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease. The grafted artery or vein bypasses (that is, goes around) the blocked portion of the coronary artery. So it needs treatment as soon as possible.
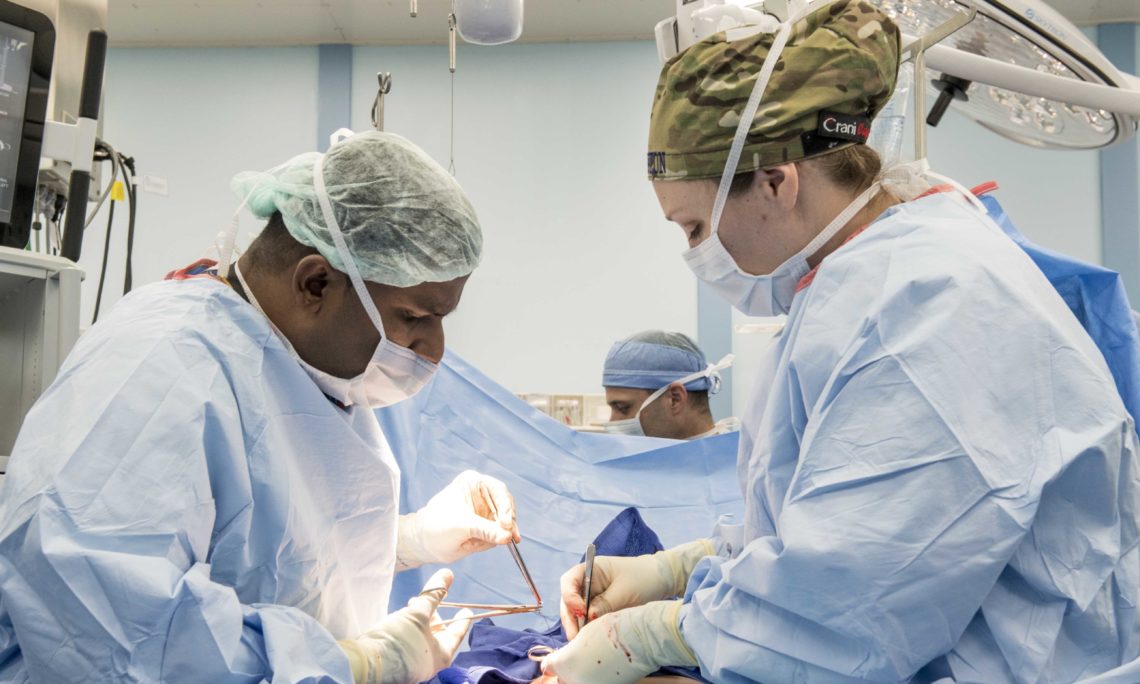
Before the angioplasty procedure begins, you will receive some pain medicine. You may also be given medicine that relaxes you, and blood-thinning medicines to prevent a blood clot from forming. The doctor will use live x-ray pictures to carefully guide the catheter up into your heart and arteries. Liquid contrast (sometimes called "dye," will be injected into your body to highlight blood flow through the arteries. This helps the doctor see any blockages in the blood vessels that lead to your heart.
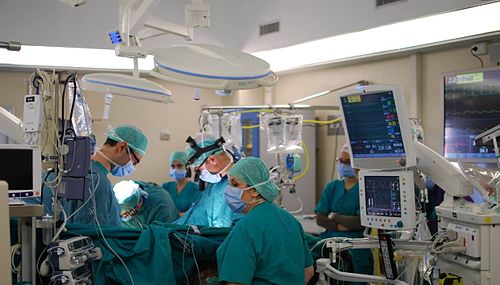
An aortic aneurysm is a bulge in your aorta, the main blood vessel that carries blood from your heart to the rest of your body. Arteries usually have strong, thick walls. But sometimes, certain illnesses or problems with your genes make them weak. The force of your blood constantly pushing against those weakened walls can make them swell. The result is a balloon-like bulge, called an aneurysm. If it grows too large and bursts, it can become an emergency. So it needs treatment as soon as possible.